DLP
Data Leak Prevention (DLP) helps protect sensitive information from leaving your organization via email. It automatically checks outgoing messages for content defined by your company’s policy. Examples include credit card or bank account numbers, large lists of email addresses, government IDs, and other personal or confidential information. DLP works as a filter on outgoing email. If a message matches the policy, one of several actions may occur. You may receive a warning, the message may be sent only if it can be encrypted, the message may be placed in quarantine for review, or the message may be blocked. If encryption is required but not possible, the message will not be delivered. In those cases, you may be notified, and your organization’s DLP managers may also receive a notification. To protect privacy, details shown in notifications may be masked.
DLP can monitor email at various levels:
email body content
email headers
email attachments of various types
nested attachments of various types
CipherMail DLP scans outgoing email for sensitive content. It analyzes the message body, attachments, and nested attachments when those parts are in text-based formats such as plain text, HTML, or XML. Filtering of binary documents like PDF, DOC, and XLS is planned for a future release.
Configuration is done in the CipherMail Web GUI. You define DLP patterns that describe what to look for in messages. Patterns can be as simple as a list of keywords and phrases that must not appear, or as advanced as regular expressions that match structured data such as credit card numbers or national identifiers. You can set a threshold to define how many matches are needed before a rule triggers, choose what happens when a rule matches (warn, require encryption, quarantine, or block), and optionally delay the action until after an encryption attempt. If you are concerned about exposing matched content in notifications (for example a credit card number), you can use a match filter to mask the sensitive part in the message that is sent to users or DLP managers.
DLP can be enabled at three levels: gateway, domain, and individual user. Settings are inherited in the same way as encryption policies, so domains inherit from the global gateway settings and users inherit from their domain. This makes it easy to enforce organization-wide rules while allowing exceptions for specific domains or users. For example, some users may be allowed to send certain information that others cannot. A typical quick setup is to create one or more DLP patterns (for example, keywords like confidential or secret), assign those patterns at the appropriate level (global, domain, or user), and choose the action Must Encrypt so any matching email must be encrypted. If an email cannot be encrypted when Must Encrypt applies, it will not be sent and the sender will be notified. For stricter policies, use Quarantine or Block.
Express setup
To configure DLP for basic keyword filtering, follow these steps. You will create a filtering pattern and apply it to the global settings so that the pattern is used by all gateway domains
Open the “DLP Available Patterns” page
Add a new DLP pattern
The first field is the name of the pattern. Type “My first pattern”, or any pattern name you find appropriate
Under “Description” type a description of your pattern, or leave empty
Under “Regular expression” type the following:
confidential|secretor any sequence of words, separated by a vertical bar. The vertical bar is important, it separates the keywords. If you omit the bars, the words will be used as a sentence to filter forKeep “Threshold” set to its default value (0)
Keep “Validator” set to its default empty value
Under “Action”, select “Must Encrypt”. This means that if the pattern matches, the message must be encrypted. The other options will be explained later
Keep “Match Filter” set to its default empty value
Keep “Delay evaluation” set to its default value (disabled)
Now click Save
To enable the new pattern, open the “DLP Selected Patterns” page . From the “Available Pattern” list, select the newly added pattern and click Add and then Save
Enable DLP scanning . Enable DLP Enabled and click Save
With “My first pattern” enabled, any outgoing email that contains the keywords
confidential or secret is marked as Must Encrypt. The message will be sent
only if encryption succeeds. If encryption is not possible, delivery is blocked
and the sender is notified.
Patterns
You can view and manage all Data Loss Prevention (DLP) patterns on the “DLP Available Patterns page” . From there, you can create new patterns, edit existing ones, enable or disable patterns, and remove patterns that are no longer needed.
For easier administration and policy application, assign patterns to a pattern group. Pattern groups let you organize related patterns (for example, all payment card patterns) and reference the entire group when configuring DLP rules or policies. Changes to a pattern or its group membership take effect for all policies that use that group.
Hint
The DLP Policy Patterns list shows all patterns that have been defined, but patterns in this list are not active by default. To use a pattern, assign it in Global Settings or to a specific domain or user.
Pattern
A new pattern can be added by clicking from the “DLP Policy Patterns” page.
A pattern has the following fields:
- Name
Enter a unique name for the pattern. This field is required.
- Description
The description should explain in brief terms what this pattern actually does, i.e., what it scans for and what the action is.
- Regular expression
The regular expression that will be matched against the content of the email. This should be a valid regular expression. As explained later, the text from the email is converted to lowercase before scanning. The regular expression should therefore only contain lower case characters. This field is required.
- Example:
The following regular expression will match if the email contains the word
confidential:confidential- Example:
The following regular expression will match if the email contains the word
confidentialorsecret:confidential|secret
- Example:
The following regular expression will match if the email contains a master card CC in 4-4-4-4, 4 4 4 4 or 16 format:
\b5[1-5]\d{2}\s?-?\s?(?:\d{4}\s?-?\s?){3}\b
Hint
For performance reasons, some words will be removed from the email before scanning (see “skip list”). If a pattern should match a complete sentence, make sure that the pattern does not contain words from the “skip list”.
- Threshold
Threshold sets how many times a pattern must be detected before its action runs. For example, if you add a pattern that checks for email addresses and you want the action to run only when more than 5 email addresses are found, set Threshold to 5.
Note
Using a pattern that detects email addresses
(?:\b|")[\"a-z0-9!#$%&'*+/=?^_`{|}~.-]{1,64}@[a-z0-9.-]{1,64}\.[a-z]{2,4}\b
with a “Threshold” of 10 and a “block” rule, you can prevent the gateway
from sending email in case the sender used the Cc field instead of the Bcc
field (prevent email address leakage).
- Validator
Some identifiers include built‑in check digits or other structure that a simple pattern match cannot verify. For example, many payment card numbers use the Luhn checksum. In these cases, matching the format with a regular expression is only the first step. A validator performs an additional check on the matched text to confirm it is structurally valid according to the relevant rule (such as a checksum algorithm).
Using a validator reduces false positives: values that look correct at a glance (because they match the pattern) but are actually invalid are filtered out by the extra validation step. This approach is useful for formats like credit card numbers, national identifiers, and bank account numbers, where spaces or dashes may be present and a checksum determines validity.
Note that passing validation means the identifier is structurally correct, not that it is active, issued, or belongs to a specific person or account.
The following validators are supported:
- BSN
Checks whether the matched part is a valid “Burgerservicenummer” (see https://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Burgerservicenummer for more information about BSN).
- DEA
Checks whether the matched part is a DEA Registration Number (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DEA_number for more information about DEA number).
- Luhn
Checks whether the matched part validates against the Luhn checksum (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luhn_algorithm for more information about the Luhn algorithm).
- NPI
Checks whether the matched part validates against a National Provider Identifier (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Provider_Identifier for more information about NPI).
Note
Additional validators can be added to the system. For example validators that match certain company specific values. Please contact us if additional validators are required.
- Action
When the pattern matches and the threshold is reached, the system carries out the action you configured. The following actions are supported:
- Warn
The Warn action sends a warning email. Depending on your DLP settings, the warning is sent to the message sender, the DLP managers, or both.
- Must Encrypt
Use Must Encrypt to require encryption for the email. If the email cannot be encrypted, it will not be sent, and you will be notified.
- Quarantine
Selecting Quarantine moves the email to a secure quarantine area. Depending on your DLP configuration, notifications may be sent to the sender and/or to your organization’s DLP managers.
- Block
Quarantine prevents the email from being delivered. The sender will receive a notification.
- Match Filter
When a message is blocked or quarantined, you will receive a notification that shows the portion of the message that matched a rule. If this portion includes sensitive information, such as a credit card number, it can be hidden using a match filter. Currently, only the Mask filter is available. The Mask filter replaces the characters in the matched portion with asterisks (*).
- Delay evaluation
If you enable Delay evaluation, the action is executed only when the gateway cannot encrypt the email. This is especially useful for DLP quarantine rules: because DLP checks run before encryption, a normal quarantine rule would trigger before the gateway has a chance to encrypt. With Delay evaluation turned on, the quarantine action is deferred and runs only if encryption fails, allowing messages that can be encrypted to proceed without quarantine.
Groups
A pattern group is a named collection of existing patterns. For example, you can create an IBAN group that includes all patterns needed to match country-specific IBAN formats. Using a group makes it easier to apply multiple patterns at once to global settings, a specific domain, or an individual user.
A new group can be added by clicking from the “DLP Available Patterns” page.
- Name
Enter a unique name for the pattern. This field is required.
To add patterns to the group, select a pattern from the list of available pattern and click Add from the selection menu.
Text normalization
To make it easier to write patterns and to improve scanning performance, all extracted text is normalized before analysis. Normalization ensures the text has a consistent, predictable form so your patterns are simpler and faster.
The normalization process includes:
All carriage returns and line feeds are replaced with spaces.
Consecutive spaces are trimmed to one space.
All characters are converted to lowercase.
The text is Unicode normalized (NFC).
Words from the skip list are removed.
Note
Because all text is converted to lowercase, any literal text used in one of
the patters should be written in lowercase. For example, if the text to
match is this is converted to LOWERCASE, the pattern matching the word
lowercase should be written in lowercase capitals.
Skip list
To speed up scanning, we automatically remove certain common words from the extracted text before processing. By default, the skip list includes the 100 most frequently used English words.
The skip list can be managed using the the cli:
ciphermail-cli dlp skip-list get
ciphermail-cli dlp skip-list set <file>
Selecting patterns
DLP patterns are not enabled automatically. A pattern becomes active only after you assign it to a scope: global settings, a specific domain, or an individual user.
How inheritance works:
Domains inherit DLP patterns from the global settings unless you explicitly assign patterns to that domain.
Users inherit DLP patterns from their domain unless you explicitly assign patterns to that user.
An explicit assignment at a lower level overrides inheritance from higher levels.
How to assign DLP patterns:
Open the settings for the scope you want to configure:
Global settings, or
A specific domain, or
An individual user
Open DLP pattern selection page
Choose the patterns you want to assign from the “Available Patterns” and confirm by clicking Add from the selection menu
Click Save
DLP settings
DLP settings can be configured at the global, domain, or user level.
DLP Enabled 

When enabled, DLP checks are applied to emails sent to external domains.
DLP managers
Enter a comma-separated list of email addresses for DLP managers. When settings such as Warning to DLP managers or Quarantine to DLP managers are enabled, these recipients will receive notifications when a DLP rule is violated.
Send Warning To Originator 
If this option is enabled and a DLP warning rule is triggered, the sender will receive a warning notification email.
Send Warning To DLP Managers 
If this setting is enabled and a DLP warning rule is triggered, an email notification will be sent to the DLP managers.
Send Quarantine To Originator 
When enabled, if a DLP quarantine rule is triggered, the sender receives a quarantine notification email.
Send Quarantine To DLP Managers 
When enabled, DLP managers receive a notification email whenever a DLP quarantine rule is triggered.
Send Block To Originator 
When this option is enabled and a DLP block rule is triggered, a block notification email is sent to the original sender.
Send Block To DLP Managers 
When enabled, if a DLP block rule is triggered, the system sends a block notification email to DLP managers.
Send Error To Originator 
When this option is enabled and a DLP error occurs, the sender will receive an error notification email.
Send Error To DLP Managers 
When this option is enabled, DLP managers receive an email notification if a DLP error occurs.
Quarantine On Error 
If DLP scanning fails (for example, because the message is invalid), the email is placed in quarantine.
Quarantine On Failed Encryption 

When enabled, emails that cannot be encrypted are automatically moved to quarantine.
Send Release Notification To Originator 
When enabled, if a quarantined email is released, a notification email is sent to the original sender.
Send Release Notification To DLP Managers 
When this setting is enabled, DLP managers receive a notification email whenever a quarantined message is released.
Send Delete Notification To Originator 
When this option is enabled, the sender will receive a notification email if their quarantined message is deleted.
Send Delete Notification To DLP Managers 
When this option is enabled, deleting an email from quarantine triggers a notification email to the DLP managers.
Send Expire Notification To Originator 
When enabled, if a quarantined email expires, a notification is sent to the original sender.
Send Expire Notification To DLP Managers 
When enabled, DLP managers receive a notification email when a quarantined message expires.
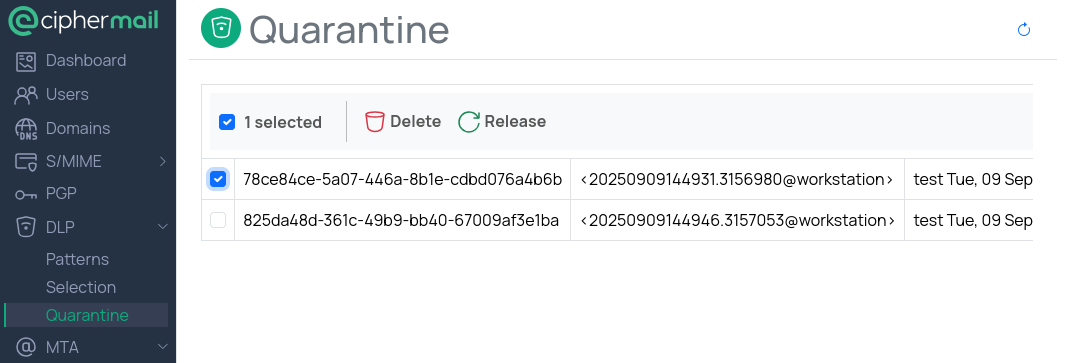
Quarantine
When a Data Loss Prevention (DLP) rule that enforces quarantine is triggered, the message is not delivered to the recipient. Instead, it is placed in the quarantine queue for review . The system then sends a notification to the original sender and/or to the designated DLP managers, depending on your configuration. The notification may include the reason the message was quarantined. While a message is in quarantine, no content is delivered to the intended recipients.
Quarantined messages remain in the system until a DLP manager reviews and releases or deletes them. Depending on your policy settings, notifications can be enabled or disabled for specific audiences.
Expiration
If a quarantined email is not deleted or released within five days, it will expire and you will receive a notification.